RBI’s Revolutionary Financial Inclusion and Trade Settlement Reforms: Strengthening India’s Economic Foundation
Introduction: A New Chapter in India’s Financial Evolution
The Reserve Bank of India has embarked on an ambitious journey that will reshape the nation’s financial landscape forever. In August 2025, the central bank unveiled a comprehensive reform package that represents far more than policy adjustments—it’s a strategic transformation designed to democratize financial services while positioning the Indian rupee as a global trade currency. These groundbreaking initiatives combine the power of grassroots financial inclusion with the sophistication of international currency mechanisms, creating a dual pathway to economic empowerment and global recognition.
India’s Financial Inclusion Index has witnessed remarkable growth, climbing from 43.4 in 2017 to an impressive 67.0 in 2025—a testament to the nation’s unwavering commitment to bringing every citizen into the formal financial system. This isn’t just about numbers; it’s about millions of families gaining access to dignity, opportunity, and economic security for the first time in their lives.
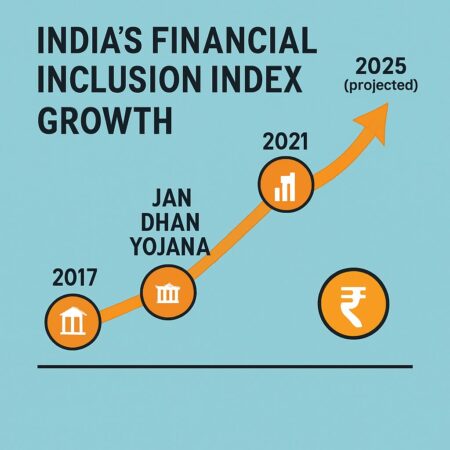
Table of Contents
- Revolutionary Consumer-Centric Reforms: Banking at Your Doorstep
- The Doorstep Banking Revolution: Transforming Rural Finance
- Simplifying Life’s Most Difficult Moments: Streamlined Settlement Procedures
- Empowering Every Indian Investor: Enhanced RBI Retail Direct Platform
- India’s Financial Inclusion Success Story: A Decade of Unprecedented Progress
- Rupee Internationalization: Breaking Currency Barriers
- Special Rupee Vostro Accounts: The Gateway to Global Trade
- Economic and Strategic Implications: Building Tomorrow’s Financial Infrastructure
- Challenges and Future Trajectory
- Conclusion: A Foundation for Inclusive Prosperity
1. Revolutionary Consumer-Centric Reforms: Banking at Your Doorstep
The RBI’s three consumer-centric schemes represent a fundamental shift in how financial services are delivered to India’s vast population. These aren’t merely administrative improvements—they’re revolutionary approaches that recognize the diverse needs of India’s geography, demographics, and economic realities.
The Three Pillars of Consumer-Centric Reform:
- Doorstep Re-KYC and Financial Services Camps
- Standardized Settlement Procedures for Deceased Account Holders
- Enhanced RBI Retail Direct Platform with Auto-Investment Features
Each of these initiatives addresses real-world problems that millions of Indians face daily. From the aged farmer in a remote village who struggles to visit a bank branch, to the urban family dealing with the loss of a loved one, to the young professional seeking simple investment opportunities—these reforms touch every segment of society.
2. The Doorstep Banking Revolution: Transforming Rural Finance
Bringing Banks to the People, Not People to Banks
Imagine this scenario: Ramesh, a 65-year-old farmer from a village in Uttar Pradesh, opened his Jan Dhan account in 2014 but hasn’t updated his KYC in years. The nearest bank branch is 15 kilometers away, and traveling there means losing a full day of work. Under the old system, Ramesh might have let his account become dormant, cutting himself off from financial services entirely.
Today, thanks to RBI’s doorstep banking initiative, a bank representative arrives at Ramesh’s village with a mobile banking unit. In less than 30 minutes, Ramesh’s KYC is updated, he’s enrolled in insurance schemes, and he’s learned about new banking services—all without leaving his village.
The Numbers Tell an Incredible Story
The early results of this initiative are nothing short of extraordinary. During just the first month of the campaign, the banking system achieved:
- 1.05 lakh camps conducted across Gram Panchayats nationwide
- 6 lakh new PMJDY accounts opened at people’s doorsteps
- 7 lakh enrollments under Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (life insurance)
- 12 lakh enrollments under Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana (accident insurance)
- 3 lakh enrollments under Atal Pension Yojana (pension scheme)
- 14.22 lakh bank accounts completed Re-KYC process
These figures represent more than statistics—they represent millions of Indians gaining access to financial security, insurance coverage, and retirement planning for the first time.
The Comprehensive Service Model
Each doorstep banking camp functions as a complete financial services center, offering:
Immediate Services:
- Re-KYC updates for existing account holders
- New account opening under PMJDY
- Grievance resolution on the spot
- Basic financial literacy education
Insurance and Protection Services:
- Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (PMJJBY): ₹2 lakh life insurance for just ₹330 annually
- Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana (PMSBY): ₹2 lakh accident insurance for ₹12 annually
- Atal Pension Yojana (APY): Guaranteed pension ranging from ₹1,000 to ₹5,000 monthly
Real-World Example:
Sunita, a domestic worker from a village in Maharashtra, attended a doorstep banking camp in July 2025. She not only updated her KYC but also enrolled in PMSBY for accident coverage and APY for her retirement. The total annual premium for both schemes: just ₹342. For less than ₹30 per month, Sunita now has accident insurance and guaranteed pension security.
3. Simplifying Life’s Most Difficult Moments: Streamlined Settlement Procedures
The Current Pain Point: A System That Adds Grief to Grief
When Anjali’s father passed away unexpectedly in Mumbai, she expected the emotional challenge of losing a parent. What she didn’t expect was spending months navigating different procedures at multiple banks, each with its own set of requirements, forms, and timelines. One bank required a succession certificate, another accepted a death certificate, and a third demanded additional affidavits. The process was not only time-consuming but also expensive and emotionally draining.
This experience is unfortunately common across India. Families dealing with the loss of a loved one often find themselves trapped in bureaucratic complexities when trying to access bank accounts, safe deposit lockers, or other financial assets.
The Revolutionary Solution: One System, Universal Standards
The RBI’s new standardized framework will transform this experience entirely. Instead of navigating different procedures at different banks, families will encounter:
Uniform Documentation Requirements:
- Single set of required documents across all banks
- Standardized forms and procedures
- Clear timelines for processing (no more indefinite delays)
- Simplified procedures for nominees, legal heirs, and survivors
Comprehensive Coverage:
- Deposit accounts (savings, current, fixed deposits)
- Safe deposit lockers and their contents
- Articles held in safe custody
- Insurance proceeds held by banks
- Mutual fund investments through banks
Real-World Impact Example:
Under the new system, when Priya’s mother passes away in Chennai, she’ll need to submit the same set of documents to all three banks where her mother held accounts. Each bank will follow identical procedures and timelines, eliminating the confusion and stress that families currently experience.
Specific Benefits for Different Family Situations
For Nominees:
- Direct access to funds within specified timelines
- Minimal documentation requirements
- No requirement for succession certificates in most cases
For Joint Account Holders:
- Immediate access to funds in jointly held accounts
- Simplified transfer procedures
- Clear guidelines for survivor rights
For Legal Heirs (when no nominee is present):
- Streamlined succession procedures
- Acceptance of family settlement deeds for smaller amounts
- Reduced court procedures for routine cases
4. Empowering Every Indian Investor: Enhanced RBI Retail Direct Platform
From Concept to Reality: Democratizing Government Securities
When the RBI launched the Retail Direct platform in November 2021, it broke a decades-old monopoly. For the first time, ordinary citizens could buy government securities directly from the central bank, without going through brokers or paying high fees. The platform was revolutionary, but it was just the beginning.
The August 2025 enhancements have transformed this platform into a comprehensive investment ecosystem that makes government securities as accessible as opening a savings account.
The New Features: Investment Made Simple
Systematic Investment Plans (SIPs) for Treasury Bills:
- Invest as little as ₹10,000 monthly in treasury bills
- Automatic reinvestment options
- Flexible investment amounts and frequencies
- No broker fees or hidden charges
Auto-Bidding Technology:
- Set your investment preferences once
- System automatically bids on your behalf
- Reinvests maturity proceeds as per your instructions
- Available 24/7 through web and mobile platforms
Real-World Success Stories
Case Study 1: The Young Professional
Arjun, a 26-year-old software engineer in Bangalore, wants to invest ₹15,000 monthly in safe instruments. Previously, his options were limited to bank fixed deposits offering 6-7% returns. Using the enhanced Retail Direct platform, Arjun now invests in treasury bills offering market-determined returns, typically higher than bank deposits, with the safety of government backing.
Case Study 2: The Retired Teacher
Mrs. Sharma, a retired school teacher in Delhi, has ₹10 lakh from her provident fund. Instead of putting it all in a single fixed deposit, she uses the platform to ladder her investments across different maturity periods, optimizing both safety and returns.
Technical Innovation: Mobile-First Approach
The platform’s mobile app, launched in May 2024, has revolutionized access:
- User-friendly interface designed for non-technical users
- Regional language support for better accessibility
- Biometric authentication for enhanced security
- Real-time notifications for investment updates and maturities
Investment Options Available
Treasury Bills (T-Bills):
- 91-day, 182-day, and 364-day options
- Minimum investment: ₹10,000
- Returns based on market auctions
- Completely safe (government guaranteed)
Government Securities (G-Secs):
- Various maturity periods from 1 year to 40 years
- Fixed and floating rate options
- Semi-annual interest payments
- Capital appreciation potential
Systematic Investment Benefits:
- Rupee cost averaging reduces timing risk
- Disciplined investment habit formation
- Automatic reinvestment eliminates manual tracking
- Professional-grade investment tools for retail investors
5. India’s Financial Inclusion Success Story: A Decade of Unprecedented Progress
The Transformation: From Financial Desert to Financial Oasis
To understand the magnitude of India’s financial inclusion success, consider this stark contrast:
2014: The Starting Point
- Millions of Indians had never held a bank account
- Rural areas were financial deserts with no banking presence
- Women were largely excluded from formal financial systems
- Digital payments were virtually non-existent in rural areas
2025: The Achievement
- 53.14 crore accounts under Jan Dhan Yojana alone
- 99.95% of villages have banking access within 5 kilometers
- Women account for 55.6% of Jan Dhan accounts
- UPI transactions reached 55.7 billion by July 2024
The Numbers That Changed a Nation
Financial Inclusion Index Growth:
- 2017: 43.4 (baseline measurement)
- 2021: 54.2 (when systematic tracking began)
- 2024: 64.2 (accelerated growth phase)
- 2025: 67.0 (current achievement)
This represents a 54.6% improvement since 2017, demonstrating consistent progress across all dimensions of financial inclusion.
The Jan Dhan Revolution: A Detailed Analysis
Account Opening Success:
- 53.14 crore accounts opened since 2014
- 3.6-fold increase from March 2015 levels
- Average growth: Over 5 crore accounts annually
Deposit Growth Story:
- March 2015: ₹15,600 crore total deposits
- March 2024: ₹2.31 lakh crore total deposits
- 15-fold increase in deposits over 9 years
- Average account balance: ₹4,476 (nearly 4x growth from 2015)
Gender Empowerment Through Financial Inclusion
Women’s Financial Participation:
- 29.56 crore women hold Jan Dhan accounts (55.6% of total)
- Women’s account ownership has enabled:
- Direct benefit transfer of government schemes
- Independent access to financial services
- Microenterprise development opportunities
- Reduced dependence on informal lenders
Real-Life Impact:
Kamala, a vegetable vendor from rural Karnataka, received her first bank account in 2015 under Jan Dhan Yojana. Today, she receives cooking gas subsidies directly in her account, has a RuPay card for cashless transactions, and has built a savings balance of ₹25,000. Her financial independence has transformed not just her life but her family’s future prospects.
Rural India’s Banking Revolution
Geographic Distribution:
- 35.37 crore accounts in rural and semi-urban areas (66.6%)
- 1.3 million banking touchpoints mapped on Jan Dhan Darshak App
- 5-kilometer radius banking access for 99.95% of inhabited villages
Infrastructure Expansion Since 2014:
- Bank branches: 46% increase
- ATMs: 30% increase
- Banking Correspondents: Dramatic expansion to serve remote areas
- Mobile banking services: Universal coverage
Digital Payment Revolution
RuPay Card Success:
- 36.14 crore RuPay debit cards issued under Jan Dhan
- Cards enabled digital payment adoption in rural areas
- Integration with UPI created seamless payment ecosystem
UPI Transformation:
- July 2024: 55.7 billion UPI transactions
- Rural UPI adoption accelerated by Jan Dhan accounts
- Merchant payments, peer-to-peer transfers, bill payments all digitized
The JAM Trinity Impact
Jan Dhan + Aadhaar + Mobile = Revolutionary Change
- ₹3.48 lakh crore saved by eliminating duplicate and fake beneficiaries
- ₹38.49 lakh crore transferred through Direct Benefit Transfer over 10 years
- 99.5% coverage of eligible beneficiaries under various government schemes
Specific DBT Success Stories:
LPG Subsidy (PAHAL):
- World’s largest direct cash transfer program
- ₹2.61 lakh crore transferred since launch
- 31.68 crore beneficiaries covered
PM-KISAN Scheme:
- ₹2.81 lakh crore transferred to farmers
- 11.8 crore farmer families benefited
- Direct transfer eliminated intermediaries
MGNREGA Payments:
- 100% digital payments to workers
- Reduced corruption and delays
- Improved work participation rates
6. Rupee Internationalization: Breaking Currency Barriers
The Strategic Vision: Why Rupee Internationalization Matters
For decades, India’s international trade has been dominated by foreign currencies, primarily the US dollar. This dependency creates several challenges:
Economic Vulnerabilities:
- Exchange rate fluctuation risks
- Transaction costs for currency conversion
- Dependence on foreign currency availability
- Impact of global monetary policies on domestic trade
Strategic Dependencies:
- Vulnerability to international sanctions
- Limited monetary policy independence
- Reduced bargaining power in international trade
- Exposure to global financial system disruptions
The RBI’s rupee internationalization initiative addresses these challenges by creating alternative pathways for international trade and finance.
The Multi-Pronged Strategy
Phase 1: Bilateral Trade Agreements
- Starting with neighboring countries
- Focus on countries with significant trade volumes
- Building confidence through successful partnerships
Phase 2: Regional Expansion
- Extending to regional trading partners
- Creating rupee liquidity pools in key markets
- Establishing correspondent banking networks
Phase 3: Global Integration
- Broader international acceptance
- Integration with global payment systems
- Full convertibility considerations
Current Success Stories
Bangladesh Partnership:
- Bilateral rupee trade commenced in 2025
- Eastern Bank and Sonali Bank Ltd (Bangladesh side)
- State Bank of India and ICICI Bank (Indian side)
- Bangladesh becomes 19th country to trade in rupees
Russian Trade Relations:
- Operational Vostro accounts facilitate trade
- Energy imports paid in rupees
- Reduced dependency on dollar transactions
- Strategic partnership despite global pressures
Sri Lankan Economic Support:
- Rupee credit lines during economic crisis
- Essential imports financed through rupee mechanisms
- Strengthened bilateral economic relationships
The Neighboring Countries Strategy
Target Countries and Trade Volumes:
- Bangladesh: Largest trade partner in region
- Nepal: Traditional trading relationship
- Bhutan: Comprehensive economic partnership
- Sri Lanka: Strategic maritime neighbor
Combined Trade Statistics:
- $25 billion total exports to South Asia (2024-25)
- 90% concentrated in these four countries
- Ideal testing ground for rupee expansion
Regulatory Framework Evolution
FEMA Amendments 2025:
- Non-residents can open rupee accounts in overseas branches
- Indian exporters can maintain foreign currency accounts abroad
- Simplified procedures for current and capital account transactions
- Enhanced flexibility for trade settlements
Benefits for Indian Businesses:
Exporters:
- Receive payments directly in rupees
- Reduced foreign exchange conversion costs
- Eliminated currency hedging requirements
- Faster settlement processes
Importers:
- Pay suppliers in rupees from Vostro accounts
- Reduced transaction costs
- Stable pricing arrangements
- Improved cash flow management
7. Special Rupee Vostro Accounts: The Gateway to Global Trade
Understanding Vostro Accounts: The Technical Foundation
A Vostro account is essentially a bank account held by one bank on behalf of another bank in a foreign country. In the context of rupee internationalization, Special Rupee Vostro Accounts (SRVAs) allow foreign banks to hold rupee-denominated deposits with Indian banks to facilitate trade settlements.
How It Works in Practice:
- A Russian bank opens an SRVA with an Indian bank
- Russian importers pay their Indian bank in rubles
- The Russian bank credits the SRVA with equivalent rupees
- Indian exporters receive payment from the SRVA
- No dollar conversion required in the entire process
The August 2025 Revolutionary Change
Before August 2025:
- Foreign banks needed prior RBI approval for each SRVA
- Lengthy application and approval processes
- Bureaucratic delays hindering trade
- Limited scalability of rupee trade
After August 2025:
- Authorized Dealer banks can open SRVAs directly
- No prior RBI approval required
- Streamlined documentation process
- Faster implementation of rupee trade arrangements
Global Reach and Expansion
22 Countries Permitted:
The RBI has permitted banks from 22 countries to open SRVAs, including major economies and strategic partners:
Major Developed Economies:
- United Kingdom
- Germany
- Singapore
- Japan
Strategic Partners:
- Russia (operational)
- UAE
- Saudi Arabia
Regional Neighbors:
- Bangladesh
- Sri Lanka (operational)
- Nepal
- Bhutan
Emerging Markets:
- Brazil
- South Africa
- Malaysia
- Thailand
Current Operational Status
Active Accounts (as of August 2025):
- Russia: Multiple operational accounts
- Sri Lanka: Active trade facilitation
- Mauritius: Financial services hub
In Pipeline (approximately 12 countries):
- Various stages of account opening
- Documentation and compliance verification
- Expected operationalization by end-2025
Trade Volume Impact
Measurable Benefits:
- Reduced transaction costs by 2-3%
- Faster settlement times (3-5 days vs. 7-10 days)
- Eliminated currency conversion risks
- Improved cash flow for businesses
Sector-Wise Impact:
Energy Trade:
- Oil imports from Russia in rupees
- Reduced dollar dependency for energy security
- Stable pricing arrangements
Pharmaceuticals:
- Indian generic medicines exports
- Payment in local currencies
- Expanded market access
Textiles and Apparel:
- Traditional export sector beneficiary
- Competitive pricing advantages
- Faster payment cycles
Information Technology Services:
- Service exports settlements
- Reduced foreign exchange complexities
- Enhanced competitiveness
8. Economic and Strategic Implications: Building Tomorrow’s Financial Infrastructure
Domestic Economic Strengthening
Financial Inclusion as Economic Foundation:
The consumer-centric reforms create a robust domestic financial base that supports broader economic objectives:
Increased Domestic Savings:
- Formal sector savings mobilization
- Reduced dependence on informal financial systems
- Capital formation for economic development
- Insurance coverage for risk mitigation
Enhanced Consumer Spending:
- Digital payment adoption increases transaction velocity
- Easier access to credit for consumption and investment
- Multiplier effects on economic growth
- Rural purchasing power enhancement
International Economic Positioning
Reduced External Vulnerabilities:
- Lower dependence on dollar-denominated transactions
- Reduced impact of global currency volatility
- Enhanced trade financing capabilities
- Strategic autonomy in economic decisions
Trade Competitiveness Enhancement:
- Lower transaction costs for Indian businesses
- Faster settlement mechanisms
- Improved terms of trade with partner countries
- Enhanced export competitiveness
Geopolitical Implications
Strategic Autonomy:
The rupee internationalization initiative provides India with greater freedom in international relations:
Sanctions Resilience:
- Alternative payment mechanisms for strategic partners
- Reduced vulnerability to financial warfare
- Maintained trade relationships during global tensions
- Economic sovereignty enhancement
Regional Leadership:
- Currency leadership in South Asian region
- Financial integration with neighboring countries
- Enhanced soft power through financial cooperation
- Economic diplomacy tool development
Long-term Economic Benefits
Monetary Policy Independence:
- Reduced transmission of global monetary shocks
- Greater control over domestic interest rates
- Enhanced effectiveness of domestic monetary policy
- Reduced vulnerability to global liquidity conditions
Financial System Stability:
- Diversified international payment systems
- Reduced systemic risk from dollar dependency
- Enhanced resilience of banking system
- Improved financial system efficiency
9. Challenges and Future Trajectory
Implementation Challenges
Scale and Logistics:
The sheer scale of India’s financial inclusion initiative presents massive logistical challenges:
Doorstep Banking Campaign:
- Coordinating across 2.5 lakh Gram Panchayats
- Training thousands of banking personnel
- Maintaining service quality standards
- Managing rural infrastructure constraints
Technology Infrastructure:
- Ensuring reliable internet connectivity in remote areas
- Managing cybersecurity for increased digital transactions
- Integrating legacy systems with new platforms
- Maintaining system uptime and performance
Human Resource Development:
- Financial literacy education for new account holders
- Training banking staff for expanded services
- Developing local language capabilities
- Managing increased operational workload
Rupee Internationalization Obstacles
Market Confidence Building:
- Establishing rupee as reliable store of value
- Demonstrating exchange rate stability
- Building international trust in Indian financial system
- Managing perception risks
Liquidity Management:
- Ensuring adequate rupee liquidity in international markets
- Managing seasonal and cyclical variations
- Balancing domestic and international liquidity needs
- Developing hedging mechanisms for international holders
Competitive Landscape:
- Competition from established international currencies
- Emerging alternatives (digital currencies, regional currencies)
- Maintaining competitive advantages
- Adapting to evolving global financial architecture
Regulatory and Compliance Challenges
International Standards:
- Meeting international banking and finance standards
- Complying with anti-money laundering requirements
- Managing know-your-customer obligations
- Ensuring regulatory consistency across jurisdictions
Domestic Regulatory Balance:
- Balancing financial inclusion with financial stability
- Managing risks from rapid expansion
- Ensuring consumer protection
- Maintaining prudential regulations
Future Development Roadmap
Phase 1 (2025-2026): Foundation Building
- Complete doorstep banking campaign coverage
- Establish SRVA network with target countries
- Achieve standardized settlement procedures
- Expand Retail Direct platform usage
Phase 2 (2026-2028): Scale and Integration
- Achieve 70+ Financial Inclusion Index score
- Establish rupee trade with 30+ countries
- Integrate digital currency initiatives
- Develop advanced financial products
Phase 3 (2028-2030): Global Integration
- Achieve comprehensive financial inclusion
- Establish rupee as regional reserve currency
- Integrate with global payment systems
- Achieve broader international acceptance
Measuring Success: Key Performance Indicators
Financial Inclusion Metrics:
- Financial Inclusion Index progression
- Account activation and usage rates
- Digital payment adoption in rural areas
- Insurance and pension scheme coverage
Rupee Internationalization Metrics:
- Volume of rupee-denominated trade
- Number of countries with operational SRVAs
- Stability of rupee exchange rates
- International rupee reserves held by central banks
Economic Impact Indicators:
- Reduced transaction costs for businesses
- Improved trade settlement times
- Enhanced export competitiveness
- Foreign exchange reserve optimization
10. Conclusion: A Foundation for Inclusive Prosperity
The Reserve Bank of India’s comprehensive reform package announced in August 2025 represents far more than a collection of policy changes—it embodies a transformational vision for India’s economic future. These initiatives create a seamless integration of domestic financial inclusion with international monetary leadership, establishing foundations that will support India’s development aspirations for decades to come.
The Synergistic Impact
The true power of these reforms lies not in their individual components but in their synergistic effects:
Domestic Strength Enables International Leadership:
A financially included population creates a stronger domestic economy, which in turn supports a more credible international currency. When millions of Indians have bank accounts, insurance coverage, and investment opportunities, the rupee becomes backed by genuine economic activity and broad-based prosperity.
International Recognition Supports Domestic Development:
As the rupee gains international acceptance, reduced transaction costs and enhanced trade competitiveness benefit domestic businesses, creating jobs and opportunities that further strengthen financial inclusion efforts.
Transformational Outcomes
For Individual Citizens:
- Banking services at their doorstep, regardless of geography
- Simplified procedures during life’s most difficult moments
- Investment opportunities previously available only to the wealthy
- Protection through insurance and pension schemes
- Dignity and inclusion in the formal financial system
For Indian Businesses:
- Reduced costs of international trade
- Faster settlement mechanisms
- Enhanced competitiveness in global markets
- Reduced currency risks
- Access to broader financing options
For the Indian Economy:
- Reduced external vulnerabilities
- Enhanced monetary policy independence
- Stronger domestic financial system
- Improved trade balances
- Greater strategic autonomy
Global Significance
These reforms position India as a leader in inclusive economic development and monetary innovation. As other developing countries watch India’s success in financial inclusion and currency internationalization, the Indian model becomes a template for sustainable economic development that prioritizes both growth and equity.
The early indicators are overwhelmingly positive. The doorstep banking campaign’s initial success, with over 1 lakh camps conducted and millions of accounts opened and updated in just the first month, demonstrates the pent-up demand for accessible financial services. Similarly, the enthusiastic response from international partners to simplified SRVA procedures suggests growing confidence in rupee-denominated trade.
The Road Ahead
While significant challenges remain—from implementation complexities to international competitive pressures—the foundation has been laid for sustainable progress. The RBI’s approach of gradual, systematic expansion, supported by robust regulatory frameworks and continuous monitoring, provides the best chance for long-term success.
As Governor Sanjay Malhotra has noted, the process of currency internationalization is measured in decades, not years. However, every journey begins with decisive first steps, and the August 2025 reforms represent bold, strategic moves in the right direction.
The ultimate measure of these reforms’ success will not be in statistics alone, but in the transformed lives of millions of Indians who gain access to financial dignity, the enhanced competitiveness of Indian businesses in global markets, and the strengthened position of India as an economic power that prioritizes inclusion alongside growth.
The Reserve Bank of India has charted a course toward a more inclusive, resilient, and internationally integrated financial system. With sustained implementation, continued innovation, and the active participation of all stakeholders—from individual citizens to global partners—these reforms will create lasting positive change that extends far beyond India’s borders, contributing to a more stable and equitable global financial system.
India’s journey toward comprehensive financial inclusion and currency internationalization has entered a new chapter. The destination is clear: a financially empowered nation that leads by example in creating prosperity that truly reaches everyone.

Author of the Article above


